NSlookup is a command-line tool that is used to test and troubleshoot DNS servers. It allows users to query DNS servers for information, such as the IP address associated with a particular domain name or the DNS records for a specific domain.
The nslookup tool is available on most operating systems, including Windows and Linux. To use it, you simply need to open a command prompt or terminal window and type the nslookup command followed by the domain name or IP address you want to look up.
NLookup will query the DNS server and return the IP address associated with the domain name. You can also use the nslookup tool to view DNS records for a domain, such as the MX records used for email or the NS records used for DNS delegation. For more information on using the nslookup tool and all of its available options, you can consult the nslookup man page or online documentation.
Different DNS Resource types
- A Records: Mostly host records for some Domains for IPV4.
- AAA Records: Host records for domains for IPV6
- SOA Records: For more information about the domain.
- CNAME Records: Kind of redirect records, for pointing a service (mail for example) to another server (canonical name).
- MX Records: Mail server records.
- NS Records: The core nameserver record.
- TXT Records: Used for other schemas such as SPF.
How to do an NSLookup on Linux?
The NSLookup (Name server lookup) command is available on both operating systems (Linux and Windows). Only the syntax is a little bit different. Hereby are some examples of how to get the DNS name servers of the specified servers.
The basic NSLookup command:
|
1 |
Nslookup google.com |
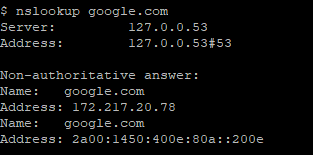
Reverse NSLookup command:
|
1 |
Nslookup 8.8.8.8 |
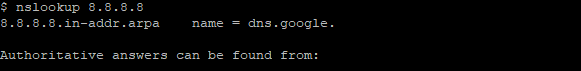
Other NSLookup commands
For querying other type records like A, AAA, SOA, CNAME, MX, NS, and TXT records you can specify a query type. Like the following example:
|
1 2 |
Nslookup -query=ns google.com Nslookup -query=mx google.com |

How to do an NSLookup on Windows.
NSLookup on Windows is almost the same command line syntax as the linux tool. So all queries discussed above are also usable on Windows. The only difference is that you need to open CMD on Windows First.
To open DOS (CMD) on Windows:
- Start, Type CMD.
- Click on the command prompt window.
- Enter “nslookup” like the commands above.